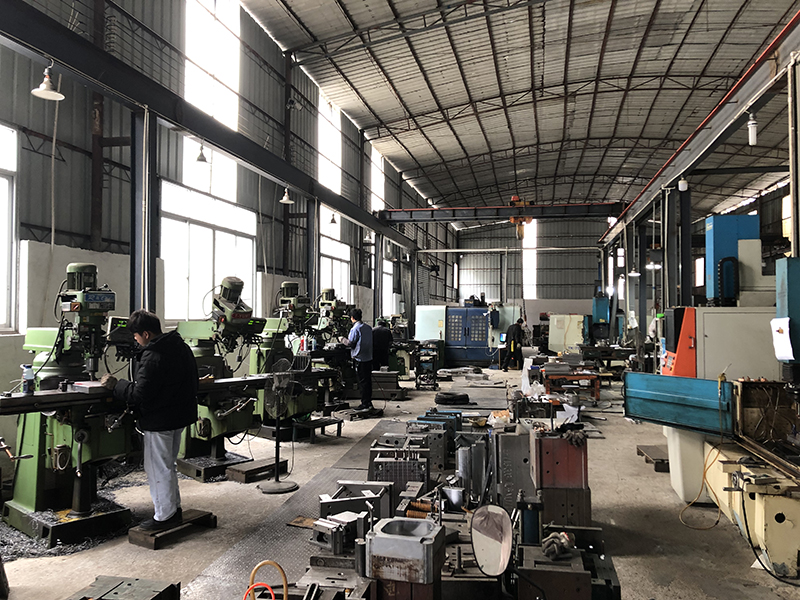
Choosing the right stamping supplier requires a comprehensive consideration of several key factors to ensure product quality, delivery time, cost, and service meet requirements. Below is a systematic selection process and evaluation criteria:
1. Define Internal Requirements
- Product Specifications: Clearly define the material (e.g., steel, aluminum, copper), thickness, dimensional tolerance, surface treatment (e.g., plating, coating), and annual demand.
- Process Complexity: Does the process require multi-stage progressive dies, precision stamping, deep drawing, or other special processes?
- Industry Standards: Does the supplier need to comply with specific industry certifications such as automotive (IATF 16949) or medical (ISO 13485)?
2. Assess Supplier’s Technical Capabilities
- Equipment and Processes:
- Check the advancement of equipment (e.g., high-speed presses, servo presses, automated production lines).
- Evaluate die design and manufacturing capabilities (Does the supplier have independent die development capabilities? What is the die life expectancy?).
- Material Management: Can the supplier provide material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH)? Do they have material testing capabilities (e.g., spectrographic analysis)?
- Technical Team: Does the supplier have experienced engineers capable of providing DFM (Design for Manufacturing) feedback?
3. Quality System Audit
- Certifications: ISO 9001, IATF 16949 are fundamental; additional industry-specific certifications may be required.
- Quality Control Processes:
- Are incoming material inspections (IQC), in-process inspections (IPQC), and outgoing product inspections (OQC) well-established?
- Do they use SPC (Statistical Process Control) or measurement equipment (e.g., CMM, projectors)?
- Defect Rate and Traceability: Review historical quality data (e.g., PPM), response time to quality issues, and corrective actions.
4. Production and Delivery Capability
- Production Capacity: Can the supplier’s maximum production capacity meet peak order demands?
- Delivery Lead Time: Standard lead times and capability for handling urgent orders.
- Supply Chain Stability: Inventory management and reliability of secondary suppliers.
5. Cost Analysis
- Price Transparency: Does the quote include mold fees, material costs, and processing fees? Are there hidden costs (e.g., mold maintenance)?
- Cost Optimization Potential: Can the supplier reduce costs through process improvements or material substitutions?
- Payment Terms: Payment structure for mold costs, bulk order discounts, and negotiation space for payment terms.
6. Service and Responsiveness
- Communication Efficiency: Language skills, time zone alignment, and professionalism of the liaison team.
- Technical Support: Can the supplier provide rapid prototyping and design optimization suggestions?
- After-sales Service: Process for handling quality issues, spare parts availability, and long-term support.
7. Industry Experience and Reputation
- Case Studies: Request case studies for similar products, particularly those with high precision or complex structures.
- Customer Reviews: Gather feedback from industry associations, trade shows, or existing clients to assess the supplier’s reputation.
- Compliance: Environmental compliance (e.g., wastewater treatment) and labor rights protection (to avoid supply chain risks).
8. Location and Logistics
- Local Advantage: Proximity of the supplier for on-site audits and reduced transportation costs and time.
- Global Presence: If exports are involved, does the supplier have experience in international delivery (e.g., customs clearance, global logistics)?
9. Risk Assessment and Backup Plans
- Single Supplier Risk: Should a backup supplier be introduced?
- Contingency Plans: Supplier strategies for handling natural disasters or supply chain disruptions.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Ensure NDA agreements are in place to protect design and mold ownership.
10. On-site Inspection and Sample Validation
- Factory Audit: Evaluate workshop management (5S), equipment maintenance, and employee compliance with operational standards.
- Sample Testing: Request samples and conduct strict tests on dimensions, hardness, surface quality, and perform salt spray or fatigue tests if necessary.
11. Contract Terms Negotiation
- Define quality standards and acceptance processes.
- Clarify mold ownership (to avoid supplier retaining molds).
- Include breach of contract clauses (e.g., penalties for late delivery or substandard quality).
Key Tools Recommended
- Supplier Rating Form: Quantitative scoring based on criteria such as technology, quality, cost, and service.
- QCDS Model: Comprehensive evaluation of Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Service.
- PPAP (Production Part Approval Process): Suitable for industries with high standards, such as automotive.
Conclusion
Prioritize suppliers that match your technical needs, offer stable quality, communicate effectively, and demonstrate potential for long-term collaboration, rather than focusing solely on low prices. It’s recommended to phase in cooperation (starting with small batch trials and progressing to larger orders) to gradually validate the supplier’s capabilities. Additionally, establish regular performance reviews to ensure continuous improvement.